Electric car chargers are not universal; they vary in terms of charging speeds, plug types, and compatibility with different electric vehicle models. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, it is important to understand that not all electric car chargers are created equal.
While there are universal charging standards such as the CCS (Combined Charging System) and CHAdeMO, which are widely adopted by many electric vehicle manufacturers, there are also proprietary charging systems specific to certain car brands. Furthermore, charging speeds can also vary, ranging from slower Level 1 chargers that offer a standard 120-volt outlet to faster Level 2 chargers, which require a 240-volt power source.
Therefore, it is crucial for electric vehicle owners to research and choose the appropriate charger that is compatible with their specific model to ensure efficient and hassle-free charging.
Types Of Electric Car Chargers
When it comes to electric cars, one of the key considerations for owners is charging. In order to power up an electric vehicle, different types of chargers are used. These chargers vary in terms of charging speed and compatibility with different electric car models. In this article, we will explore three main types of electric car chargers: Level 1 chargers, Level 2 chargers, and DC fast chargers.
Level 1 Chargers
A Level 1 charger, also known as a slow charger, is the most basic type of electric car charger. It is typically included with the purchase of an electric car and plugs into a standard household outlet, usually rated at 120 volts and 15-20 amps. This charger provides a charging speed of around 2 to 5 miles of range per hour of charging. While Level 1 chargers are convenient for overnight charging at home, they are relatively slow compared to other types of chargers and may not be suitable for those who require faster charging speed.
Level 2 Chargers
Level 2 chargers are faster and more powerful than Level 1 chargers. They require a dedicated charging station that is installed at home or at public charging stations. These chargers operate at 240 volts and can deliver charging speeds of around 10 to 60 miles of range per hour, depending on the electric car’s onboard charger. Level 2 chargers usually have a higher amperage option, such as 30 or 40 amps, allowing for faster charging. They provide a significant improvement in charging speed compared to Level 1 chargers and are popular among electric car owners who require quicker charging times.
Dc Fast Chargers
DC fast chargers, also known as Level 3 or quick chargers, are the fastest type of chargers available for electric cars. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, DC fast chargers supply direct current (DC) power to the vehicle’s battery, bypassing the onboard charger. These chargers can deliver up to 480 volts and provide high charging speeds, typically ranging from 60 to 80 miles of range in 20 minutes of charging. DC fast chargers are commonly found at public charging stations along highways or in urban areas, allowing electric car owners to quickly recharge their vehicles during long trips or when time is of the essence.
In conclusion, electric car chargers come in different types and offer varying charging speeds. Level 1 chargers are the slowest but can be used with a standard household outlet. Level 2 chargers require a dedicated charging station and provide faster charging speeds. DC fast chargers, on the other hand, offer the fastest charging times and are commonly found at public charging stations. Understanding the different types of electric car chargers can help you choose the best option for your charging needs.
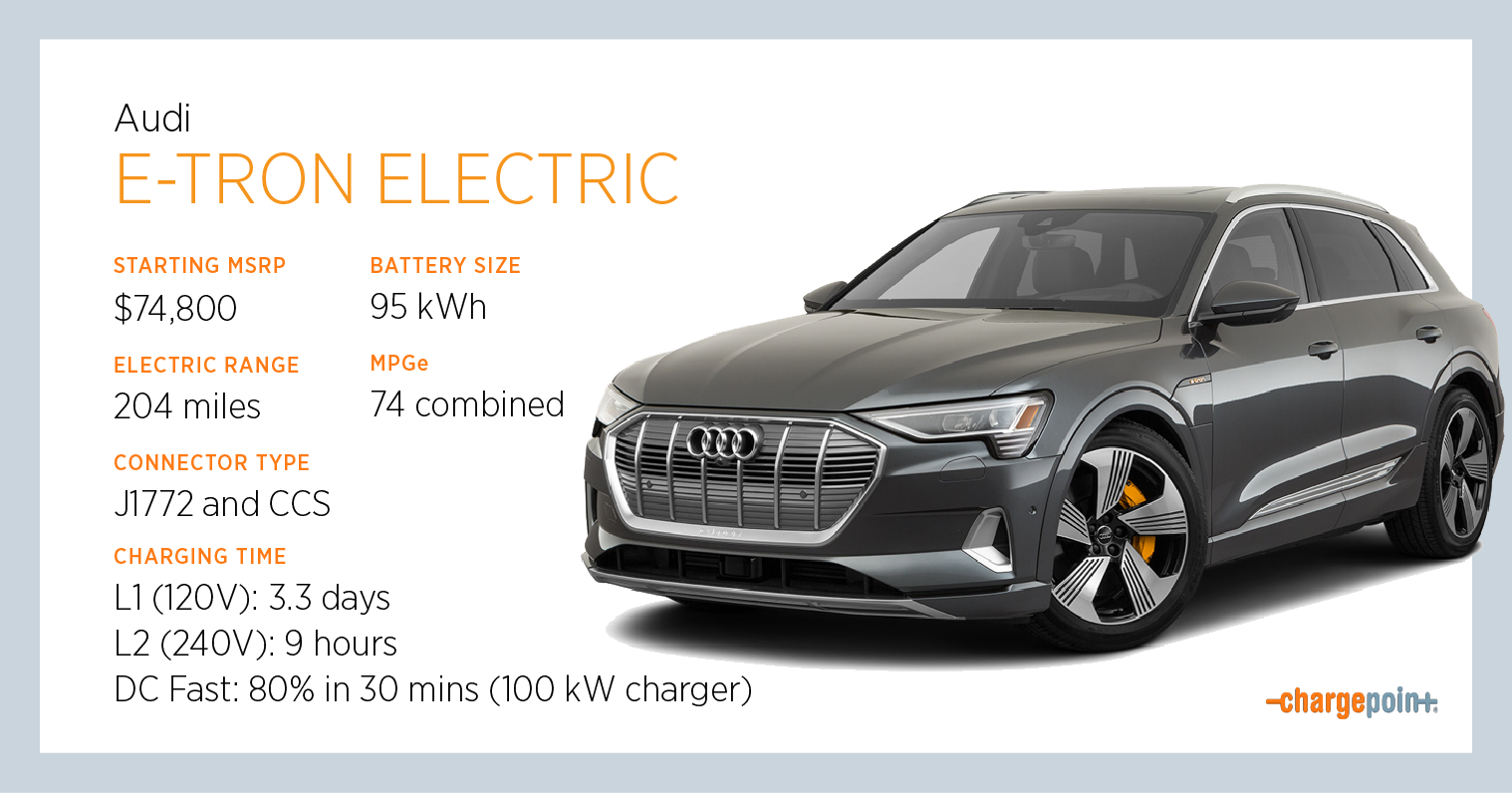
Credit: www.chargepoint.com
Compatibility Of Electric Car Chargers
Are electric car chargers universal? One of the key concerns for electric vehicle (EV) owners is the compatibility of electric car chargers. With various charger types, charging standards, and connectors in the market, it’s important to understand how they differ and whether they are compatible with your specific EV. In this article, we will explore the compatibility aspects of electric car chargers, including the different charger types by EV manufacturer, charging standards and connectors, and the use of adapters for compatibility.
Charger Types By Ev Manufacturer
Electric vehicle manufacturers often have their own proprietary charger types. This means that certain chargers are specifically designed to work with specific EV models. For example, Tesla Superchargers are compatible only with Tesla vehicles. Similarly, Nissan has its CHAdeMO chargers designed for their EV models like the Nissan Leaf.
In addition to proprietary charger types, electric vehicles are also equipped with standard charging options such as the Type 1 (J1772) connector used by most North American and Japanese EVs, and the Type 2 (Mennekes) connector widely used in Europe. These standard connectors enable compatibility with various charging stations.
Charging Standards And Connectors
Another important aspect of electric car chargers compatibility is the charging standards and connectors. There are different charging standards used worldwide, including:
- CHAdeMO: Originally developed in Japan, CHAdeMO is primarily used by Asian automakers such as Nissan, Mitsubishi, and Kia.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): CCS is commonly used in Europe and North America, and it combines both AC and DC charging capabilities.
- GB/T: GB/T is the charging standard adopted in China.
- Tesla Supercharger: Tesla’s proprietary Supercharger network uses a unique connector compatible only with Tesla vehicles.
These different charging standards come with their own specific connectors. While some EVs are compatible with multiple charging standards, others may be limited to specific standards. It’s essential to know the charging standard and connector type supported by your EV and find compatible charging stations accordingly.
Adapters And Compatibility
If your electric vehicle and the charging station have different connectors or charging standards, adapters can be used to bridge the gap. For example, if you have a Tesla vehicle and find a charging station with a Type 2 connector, you can use a Tesla to Type 2 adapter to make the connection.
However, it’s important to note that while adapters can enable compatibility, they may have limitations. They may not support high-speed charging or certain features specific to the original connector or charging standard. It’s always advisable to use compatible chargers whenever possible to ensure optimal charging performance.
In conclusion, while electric car chargers are not universally compatible, there are ways to address compatibility issues through proprietary charger types, standard connectors, and the use of adapters. Understanding the charger types by your EV manufacturer, the various charging standards and connectors, and utilizing adapters as needed will help you find the right charging solution for your electric vehicle.
Future Of Electric Car Charging
As the world continues to shift towards more sustainable modes of transportation, the future of electric car charging holds significant importance. With electric vehicles gaining popularity, the demand for a robust and universal charging infrastructure is on the rise. This presents various challenges and opportunities for the automotive industry, including standardization efforts and advancements in wireless charging technology.
Standardization Efforts
Standardization plays a vital role in ensuring the compatibility and convenience of electric car chargers. With multiple manufacturers producing electric vehicles, it is crucial to establish a common set of charging standards. This not only allows seamless interoperability between different electric vehicle models but also helps eliminate the need for multiple charging adapters.
One such standard that has gained global recognition is the Combined Charging System (CCS). This system integrates both Level 2 AC charging and fast DC charging capabilities into a single charging port. By adopting the CCS standard, electric vehicle manufacturers and charging station operators can cater to a broader range of electric vehicles, regardless of the brand.
Wireless Charging Technology
Wireless charging technology represents a significant leap towards the future of electric car charging. Imagine never having to deal with cables and plugs, but simply parking your electric vehicle over a designated charging pad. This technology utilizes electromagnetic fields to transfer energy wirelessly from the charging pad to the electric vehicle’s battery.
The development of wireless charging technology is paving the way for greater accessibility and convenience in charging electric vehicles. With advancements in efficiency and charging speeds, wireless chargers are becoming more practical for everyday use. The integration of this technology into parking lots, garages, and even roadways holds the potential to revolutionize the charging infrastructure, making electric vehicle ownership even more user-friendly.
While wireless charging technology shows promise, it is still in its early stages. Standardization efforts are crucial to ensure compatibility between different wireless charging systems. As the industry works towards establishing common standards, wireless charging is expected to become more widely accessible, making owning and charging electric vehicles easier than ever before.
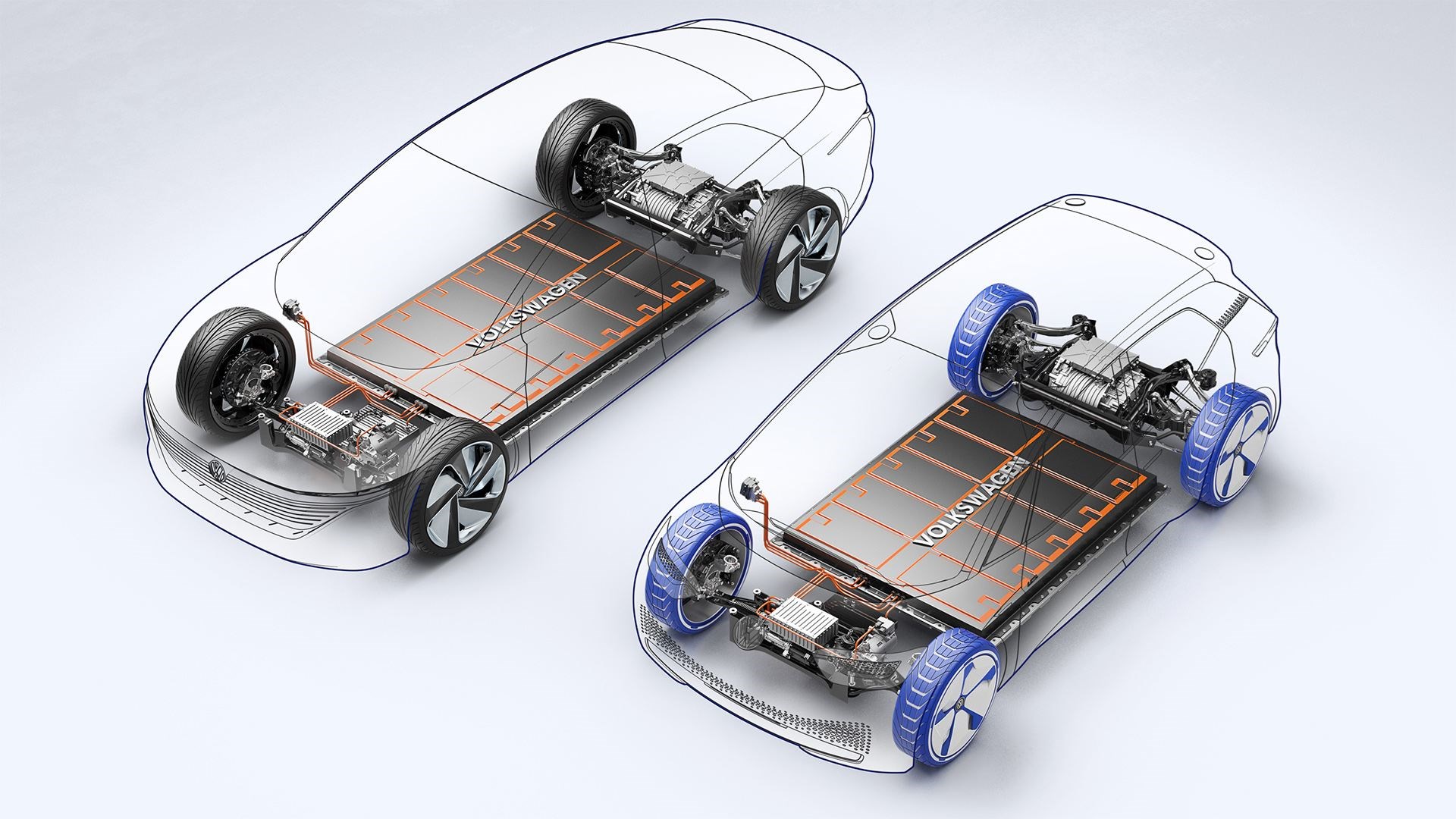
Credit: www.carmagazine.co.uk
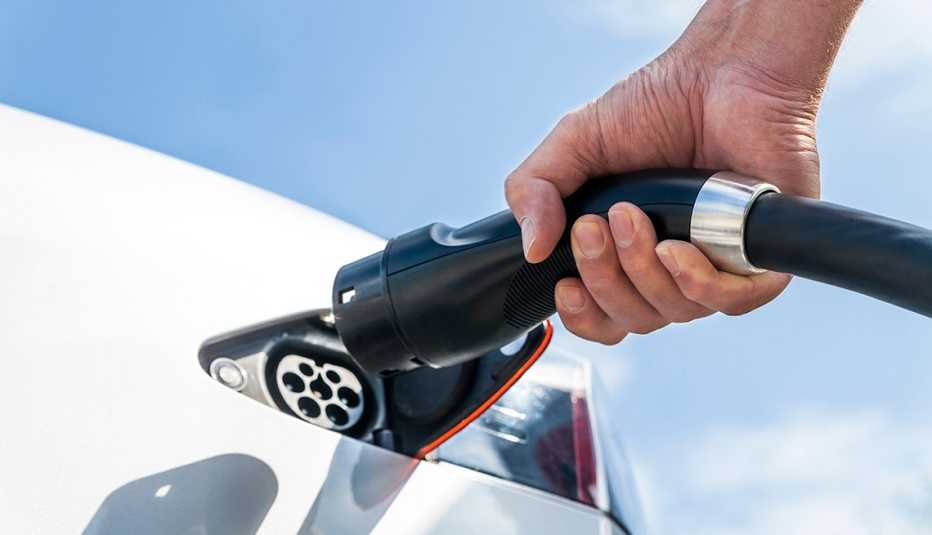

Credit: www.aarp.org
Conclusion
Electric car chargers are not universal, and various types and standards exist in the market. It is important for electric vehicle owners to ensure they have the correct charging equipment for their specific car model and adhere to the recommended charging standards.
By understanding the differences and choosing the right charger, users can optimize their charging experience and support the growth of the electric vehicle industry.